Table Of Content

The design matrix excludes the intercept term for the first factor added to the function. Only lines reflecting the first 4 parameters are drawn in the plot, representing the mean gene expression of groups A, B, C and D in lane L1 and with handling technician I. Samples are labelled by their sequencing lane (L1 or L2), and coloured black if they are processed by technician I, yellow if they are processed by technician II.
Simple linear regression
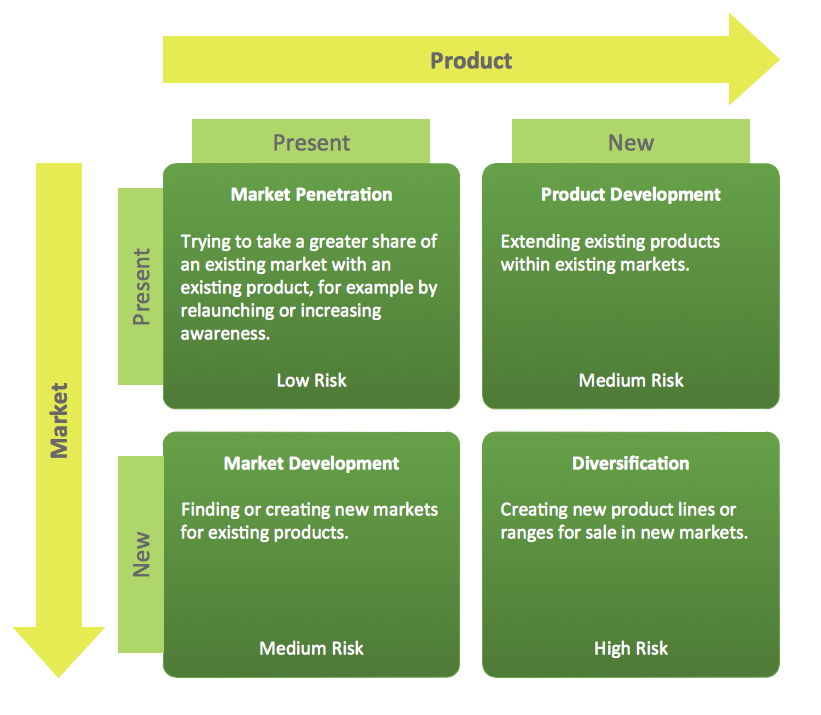
This should prompt us to consider how to set up the model properly, figuring out which factors are dependent on others, and ultimately redefining the design matrix. For example, the design matrix can be set tomodel.matrix(~0+group) instead, although we should keep in mind that some pairwise group comparisons would be confounded by batch effects, such as when comparing group A to group C. In this section, we examine several study designs that contain two or more factors as explanatory variables. We begin with an example where we convert two factors of interest into one, and then consider cases where there are factors that are not of interest.
How the design matrix is defined in linear regressions
Repeated measurements are taken from mice, as indicated by the numbers in the plot, such that label ”1” represents MOUSE1. A custom design matrix is created to model mouse IDs, treatment and timepoint (complete R code shown in the main article). Fitted lines are drawn in pink for treatment X, and in aqua for treatment Y. Solid lines represent expected gene expression at timepoint T1, and dashed lines for timepoint T2.
Try SmartDraw's House Design Software Free
Second, while the straight needle moves upward, the fabric advances one stitch and the looper moves backward to reach the back of straight needle 5 (as shown in Fig. 1c). Meanwhile the straight needle descends through the fabric for the second time and further down through the triangular loop formed by the looper, the facial suture, and the bobbin thread (as shown in Fig. 1d). In conclusion, the principle of automatic bobbin exchange technology is relatively simple and reliable, but it cannot fundamentally solve the problems of interruption of thread traces and time loss caused by many stoppages.
Accounting for factors that are not of interest
At the same time, the mechanism identity condition is used to avoid the elimination calculation of some intermediate variables, improve computational efficiency, and ultimately obtain the spatial displacement equations of tip P. At present, a lot of beneficial research has been conducted worldwide on automatic bobbin exchange devices and the innovative design of the thread-hooking mechanism, meeting the large supply of bobbin thread. Essentially, the automatic bobbin exchange device is to use manipulators to replace the empty bobbin with a full one by simulating the process of manually exchanging the bobbin during machine stopping. Hu et al. (2015) in China designed an automatic bobbin thread replacement system based on CAN-BUS (Controller Area Network-BUS), which improved the expandability and flexibility of the system, but the efficiency improvement was limited. Philippe Mall and Kinoshita proposed a box-magazine-type automatic bobbin exchanging device with a compact structure that can accommodate eight bobbins for replacing but only for thick bobbin thread and non-overlapping embroidered stitches (Jana, 2018).
Similar articles
Remember that the parameter will now represent the difference between the groups instead of the second group mean. Columns in the design matrix can be moved and reordered, or retrieved from another design matrix available in the Results Browser window. This allows us to use matrix algebra to find an estimator of the regression coefficients (see the lecture on linear regression to see how).
Molecular dynamics of the diffusion of natural bioactive compounds from high-solid biopolymer matrices for the design ... - ScienceDirect.com
Molecular dynamics of the diffusion of natural bioactive compounds from high-solid biopolymer matrices for the design ....
Posted: Fri, 14 Sep 2018 17:03:50 GMT [source]
The correlation between measurements taken from the same mouse is estimated as -0.05, which is considered to be quite a small correlation value. This is expected in our example since we did not program specific mouse effects into the dataset. In the case of a negative estimated correlation, the blocking variable should be removed and we can resume the usual modelling approach of accounting for thegroup fixed effect only in the design matrix. For real use cases, correlation estimates of 0.7 to 0.9 are considered high but not uncommon.
Each row represents an individual object, with the successive columns corresponding to the variables and their specific values for that object. The design matrix is used in certain statistical models, e.g., the general linear model.[1][2][3] It can contain indicator variables (ones and zeros) that indicate group membership in an ANOVA, or it can contain values of continuous variables. When performing differential expression analysis on genomic data (such as RNA-seq experiments), scientists usually use linear models to determine the direction (did expression go up or down?) and magnitude (by how much?) of the change in expression. These scientists are interested in understanding the relationship between gene expression (the “response” variable”) and variables that affect expression, such as a treatment or cell type (“explanatory variable(s)”).
We, however, refer to this model specifically as amean-reference model to distinguish it from the general model form that we use for covariate explanatory variables. The means model and the mean-reference model are equivalent models that differ in parameterisation, such that the form of the model is different but one could obtain equivalent values for the expected gene expression of wildtype and mutant from both models. Based on the analysis of the chain stitch formation principle, the design requirements for motion trajectory and posture of the hooking mechanism are proposed. The methods of direction cosine matrix and mechanism identity condition are applied in kinematics modeling and analysis of the RRSC mechanism. The optimization design model and computer-aided software are developed, then the human–computer interaction optimization method is used to obtain optimal solutions to meet working requirements.
We also discuss options for non-linear fitted models that extend beyond the simple framework of y-intercept and slope. Whilst in practice the vast majority of study designs involve only factor variables, which we have covered extensively over multiple sections, this section is useful for the occasional study where the relationship between gene expression and a given covariate is of interest. Each of the horizontal lines inFigure 1 are defined by their y-intercept (and a slope of 0), and are themselves regression models. We, however, will refer specifically to models of this type as ameans model since the model parameters represent the group means. This also allows us to differentiate these models from the general regression models applied to covariates where the y-intercept and slope can both be non-zero.
In the mechanism, the kinematic pairs between rocker 2 and the frame and linkage 1 are cylindrical pair and spherical pairs, respectively, and those between crank 0 and the frame and linkage 1 are both rotary pairs (as shown in Fig. 3). While the mechanism works, crank 0 is driven to rotate by the power input shaft, and it then drives linkage 1 for spatial compound motion to drive rocker 2. Finally, rocker 2 not only does the oscillation motion but also the reciprocation motion along the vertical direction shown in Fig. By optimizing the parameters of the thread-hooking mechanism, under the combined action of these two movements, the tip of looper 4 fixed on rocker 2 can form a motion trajectory that meets the embroidery chain stitch. The y-intercepts for treatment X and treatment Y are estimated as -0.06 and 1.09 respectively.
In the plot, data points are labelled by treatment, and a fitted line is drawn for each of the treatments. The group factor is converted from two factors representing tissue samples and cell types. The kinematic simulation analysis of the mechanism is carried out, verifying the correctness of the theoretical model and design results of the mechanism.

No comments:
Post a Comment